In this post I will share what I have learned about error handling, why it is important to use and how to write effective code in JavaScript. Good error handling makes a program user-friendly, it can also prevent data loss.
Error types
Syntax error : If I forget a semicolon or place it in the wrong place, it will be considered a syntax error.
Runtime errors: They happen during execution and happen due to unexpected conditions. One example would be trying to divide a number by zero. In JavaScript, the return value of a number divided by zero, will be infinity. This can make the code stop working.
Logical errors: When a code runs, but produces incorrect results, it is called a logical error.
User input errors: This happens when user provides invalid data. For example , if a user enters a text instead of a number into a field.
Handling strategies for user input errors
Trim() method
The trim() method in JavaScript for user input is used to remove whitespace. If a user unintentionally adds extra space or even leaves a field empty, trim() can ensure that the input is clean. It is often used, where user input is processed. If the input is not a string( but undefined, null , or a number), trim() would throw a TypeError.
Syntax:
string.trim()
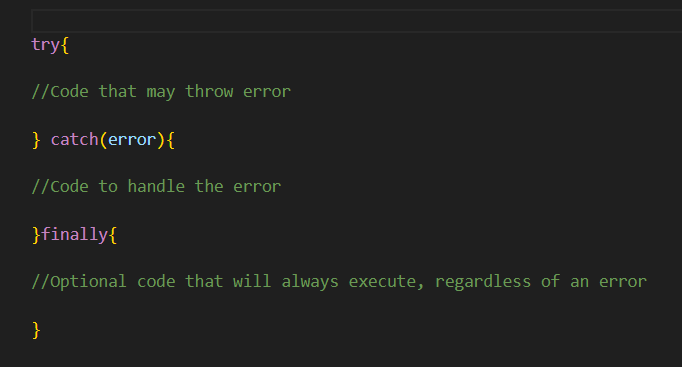
Try…catch,finally method
The try…catch, finally method is used for error handling and validation. It handles cases, where trim() is called on none-string values, to prevent runtime errors. After trimming, the input is validated to ensure it meets the requirements ( for example a field not being empty). Trim() and try…catch combined, can create robust input handling, that gracefully manages unexpected scenarios.
Syntax:
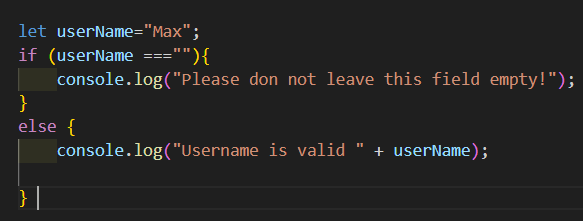
1 .Example:
This code is based on an if and else statement. A variable userName, is checked if it is empty. ( userName===””). I do not need try…catch, because this code does not throw error messages.
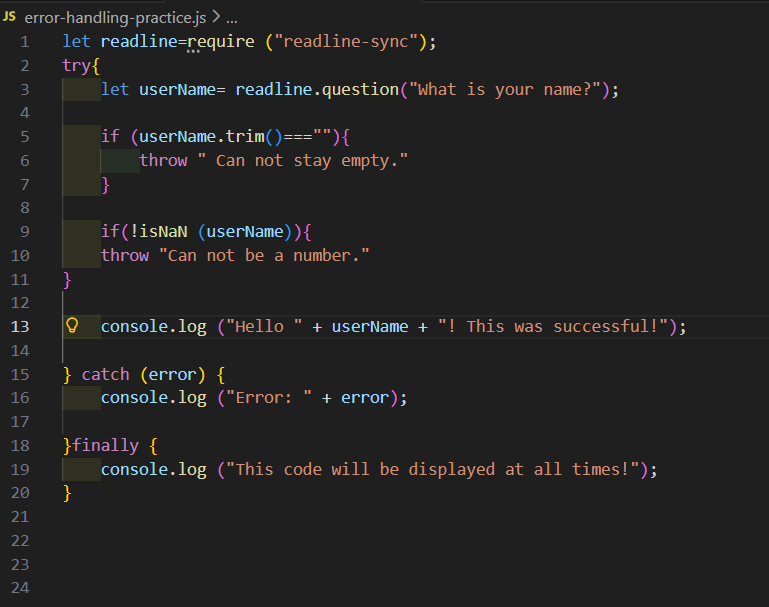
2. Example:
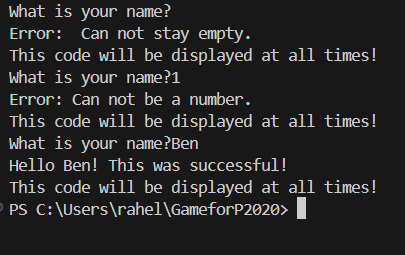
I declared a variable userName and I added trim(). If the input by the user is going to be empty, this code will throw the error message “Can not stay empty.” isNaN() is used to check if a value is not a number. In this example, I use !isNaN(userName) to throw an error if it is a number. I also placed a success message with console.log inside the try & catch block. A catch only runs, if there is an error.
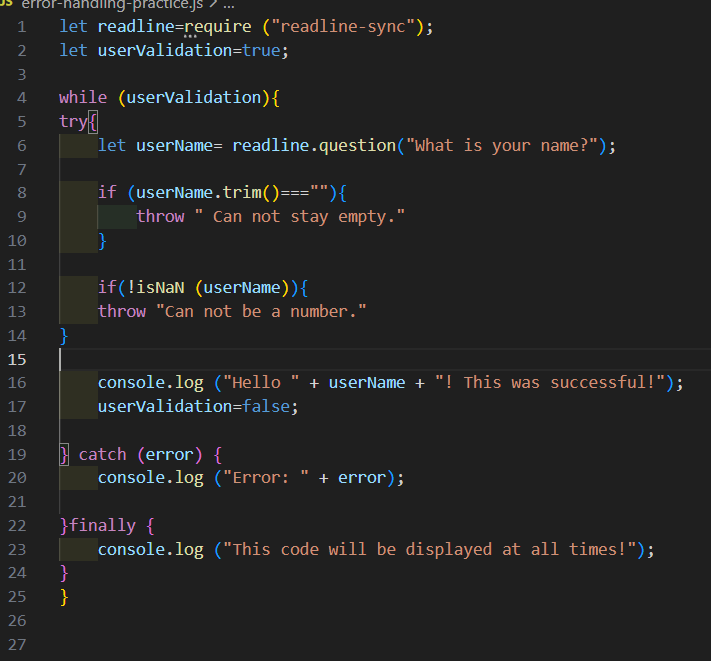
To example 2:
I have added a while loop, by placing the whole try and catch block inside the while loop. This code will be executed until no errors accure. I will be able to test every error and see if the code runs as expected. I have set userValidation= false, when a user enters a correct input. This ensures the loop will stop, once a correct input has been entered.
The output to example 2 is:
Question I came up on my learning journey and the answers I could find:
Where exactly can I place if and else statements within a try and catch error handling method?
I can write if and else if statements inside the try block. This will check conditions, before throwing an error.
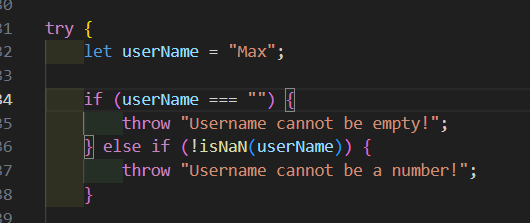
I can write if and else if statements after try…catch…finally block. If I want to write additional code once the error handling is done.
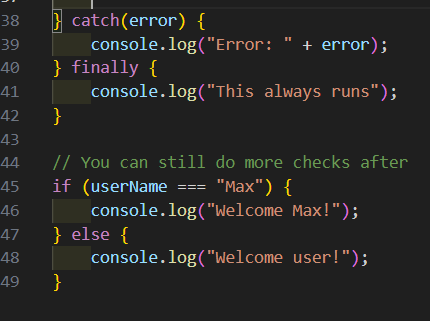
I cannot write if and else if statements inside catch or finally. Inside catch, I can handle errors and inside finally, I can insert a code that will run under any conditions.